HydroClean® plus Cavity


HydroClean® plus – The wound dressing that provides both rinsing and absorption
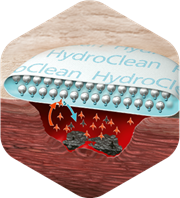
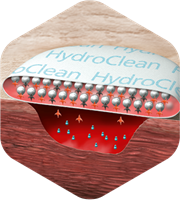
Discover the advantages of the unique Rinsing-Absorption Mechanism:
Ringer’s solution is continuously released at a constant rate to facilitate the autolysis of necrosis slough [19]
Absorbs wound exudate and debrides devitalised tissue to provide an ideal wound-healing environment [19-21]

Scroll down to watch the video

Find out more about the unique Rinsing-Absorption Mechanism of HydroClean® plus in this video:

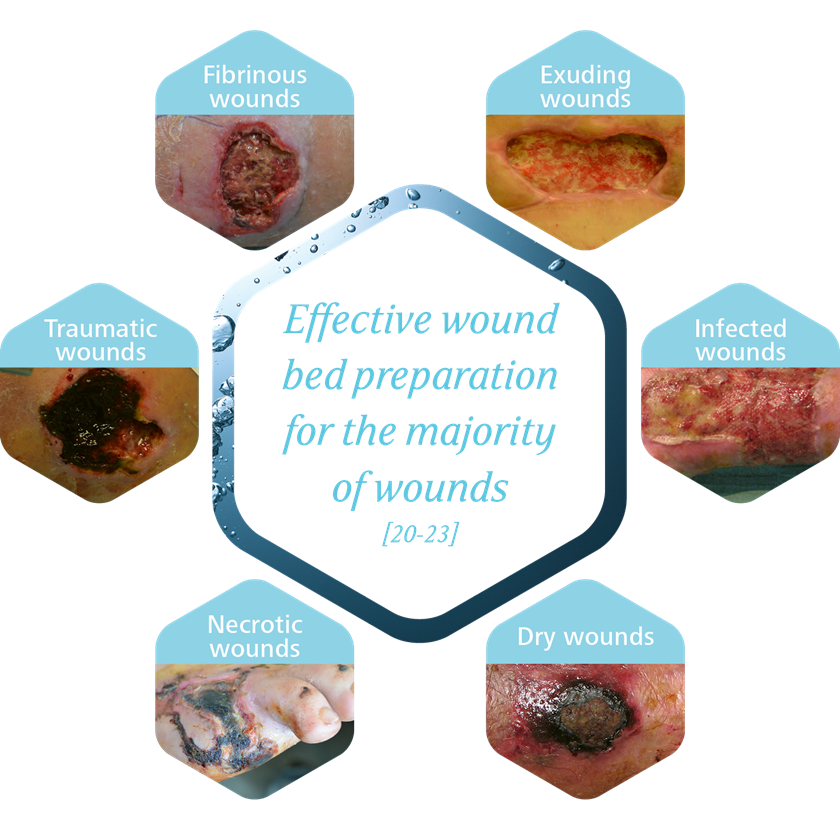
HydroClean® plus can be used on a variety of acute and chronic wounds where moist wound healing is needed. [5, 7, 12, 14]
References:
[1] Atkin, L. and Ousey, K. (2016). Wound bed preparation: A novel approach using HydroTherapy. British Journal of Community Nursing 21 (Supplt. 12), pp. S23-S28.
[2] Ousey, K. et al. (2016). HydroTherapy Made Easy. Wounds UK 12(4).
[3] Humbert, P. et al. (2014). Protease-modulating polyacrylate-based hydrogel stimulates wound bed preparation in venous leg ulcers – a randomized controlled trial. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology 28(12), pp. 1742-1750.
[4] Smola, H. (2016). Simplified treatment options require high-performance dressings – from molecular mechanisms to intelligent dressing choices. EWMA 2016. Bremen, 11-13 May, 2016.
[5] Ousey, K. et al. (2016). Hydro-Responsive Wound Dressings simplify T.I.M.E. wound management framework. British Journal of Community Nursing 21 (Supplt. 12), pp. S39-S49. [6] Spruce, P. et al. (2016). Introducing HydroClean® plus for wound-bed preparation: a case series. Wounds International 7(1), pp. 26-32.
[7] Ousey, K. et al. (2016). HydroClean® plus: a new perspective to wound cleansing and debridement. Wounds UK 12(1), pp. 94-104.
[8] Atkin, L. and Rippon, M. (2016). Autolysis: mechanisms of action in the removal of devitalised tissue. British Journal of Nursing 25(20), pp. S40-S47.
[9] Bullough, L. et al. (2016). A multi-centre 15 patient evaluation of a Hydro-Responsive Wound Dressing (HRWD) - HydroClean® plus. HydroTherapy Symposium: A New Perspective on Wound Cleansing, Debridement and Healing. London, 3 March, 2016.
[10] Scherer, R. et al. (2015). HydroTherapy®. Application study. Heidenheim: Paul Hartmann AG. [Data on file].
[11] Chadwick, P. and Haycocks, S. (2016). The use of Hydro-Responsive Wound Dressing for wound bed preparation in patients with diabetes. Wounds UK Annual Conference. Harrogate, 14-16 November, 2016.
[12] Knowles, D. et al. (2016). HydroTherapy® wound healing of a post amputation site. Wounds UK Annual Conference. Harrogate, 14-16 November, 2016.
[13] Zollinger, C. et al. (2014). HydroTherapy®. Application Study. Heidenheim: Paul Hartmann AG. [Data on file].
[14] Colegrave, M. et al. (2016). The effect of Ringer’s solution within a dressing to elicit pain relief. Journal of Wound Care 25(4), pp. 184-190.
[15] O’Brien, D. and Clarke, Z. (2016). The patient experience with a Hydro-Responsive Wound Dressing (HRWD) – HydroClean® plus. HydroTherapy Symposium: A New Perspective on Wound Cleansing, Debridement and Healing. London, 3 March, 2016.
[16] Jones, T. and McCracken, K. (2016). HydroClean® plus assists healing of leg ulcers for a patient with systemic lupus erythematosus. Wounds UK Annual Conference. Harrogate, 14-16 November, 2016.
[17] Kaspar, D. et al. (2008). Efficacité clinique du pansement irrigo-absorbant HydroClean® active contenant du polyacrylate superabsorbant dans le traitement des plaies chroniques – étude observationnelle conduite sur 221 patients. Journal des Plaies et Cicatrisations 13(63), pp. 21-24.
[18] Kaspar, D. et al. (2015). Economic benefit of a polyacrylate-based hydrogel compared to an amorphous hydrogel in wound bed preparation of venous leg ulcers. Chronic Wound Care Management and Research 2, pp. 63-70.
[19] Knestele, M (2004). The treatment of problematic wounds with HydroClean plus – tried and tested over many years in clinical practice. HARTMANN Data on file.
[20] Humbert, P. et al. on behalf of the CLEANSITE study group. Protease-modulating polyacrylate-based hydrogel stimulates wound bed preparation in venous leg ulcers a randomized controlled trial. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology 2014; 28:12, 1742-50.
[21] Kaspar, D. (2011). Therapeutic effectiveness, compatibility and handling
in the daily routine of hospitals or physicians’s practices. HARTMANN Data on file: Hydro-Responsive Wound Dressing
(HRWD) and AquaClear Technology are trademarks of HARTMANN
[22] Eming, S., Smola, H., Hartmann, B., et al. (2008). The inhibition of matrix metalloproteinase activity in chronic wounds by a polyacrylate superabsorber. Biomaterials 29: 2, 2932-2940
[23] ISBN Monograph. 978-1-944788-63-6-ISBN Services
[26] Hodgson, H. et al. (2017). A multicentre, clinical evaluation of a hydro-responsive wound dressing: the Glasgow experience. Journal of Wound Care 26(11), pp. 643-650.
[27] Davies, L. et al. (2017). An Assessment of Biofilm Disruption and Bacteriostatic Capabilities of an Autolytic Debridement Dressing. Wounds UK Annual Conference. Harrogate,
13-15 November, 2017.